A domain name is a website’s address on the internet. It helps users find and access websites easily.
Have you ever wondered how you navigate the vast world of the internet? A domain name is your key. It’s like a home address but for websites. You type it in, and it takes you to your desired site. But how does it work?
Understanding domain names is crucial for anyone who wants to create a website or simply surf the web. In this blog post, we will explore what domain names are, how they function, and why they are essential. This knowledge will give you a better grasp of the internet and how you interact with it daily.
Credit: help.northwestmediacollective.com
Introduction To Domain Names
Welcome to the world of domain names! If you’re new to this topic, don’t worry. We’ll break it down into simple terms. A domain name is like the address of a website. It’s what people type in the search bar to visit a website. Just like your home address tells people where you live, a domain name tells browsers where to find a website.
Basic Definition
A domain name is a unique string that identifies a website. Think of it as a nickname for a website’s IP address. The IP address is a series of numbers, like 192.168.1.1, which is hard to remember. So, we use domain names instead, like example.com.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Domain Name | The address where users can access a website. |
| IP Address | A numerical label assigned to each device connected to a network. |
Importance Of Domain Names
Domain names are crucial for establishing an online presence. They make it easy for users to remember and access a website. Imagine trying to remember a long string of numbers instead of a simple name.
- Branding: A domain name reflects your brand and makes it easy to find you online.
- Trust: A professional domain name builds trust with your audience.
- SEO: A keyword-rich domain name can help improve search engine rankings.
Investing in a good domain name is essential. It helps in building credibility, enhancing user experience, and boosting SEO efforts.
Components Of A Domain Name
The components of a domain name are essential for understanding how the internet works. Each part of a domain name has a specific function. These components help identify and locate websites on the internet. Let’s explore the key elements: the Top-Level Domain and the Second-Level Domain.
Top-level Domain (tld)
The Top-Level Domain (TLD) is the last part of a domain name. For example, in www.example.com, the TLD is .com. TLDs are categorized into different types:
- Generic TLDs (gTLDs): These include common extensions like .com, .org, and .net.
- Country Code TLDs (ccTLDs): These are specific to countries, such as .uk for the United Kingdom or .jp for Japan.
- Sponsored TLDs (sTLDs): These are specialized domains like .gov for government entities or .edu for educational institutions.
Choosing the right TLD is important. It can affect your website’s credibility and audience reach.
Second-level Domain
The Second-Level Domain is the part of the domain name that comes before the TLD. In www.example.com, the Second-Level Domain is example. This part is unique to your website. It often reflects your brand or business name. For instance:
- www.google.com – Here, google is the Second-Level Domain.
- www.bbc.co.uk – In this case, bbc is the Second-Level Domain.
Choosing a memorable and relevant Second-Level Domain is crucial. It helps users find your site easily.
How Domain Names Work
Understanding how domain names work is essential for navigating the internet. Domain names are human-readable addresses used to access websites. They are a key part of the internet infrastructure.
Domain Name System (dns)
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the backbone of the internet. It translates domain names into IP addresses. An IP address is a unique string of numbers. Computers use these numbers to identify each other on the network.
DNS makes it easier for users to find websites. Instead of remembering long strings of numbers, users remember simple names. For example, “example.com” instead of “192.0.2.1”.
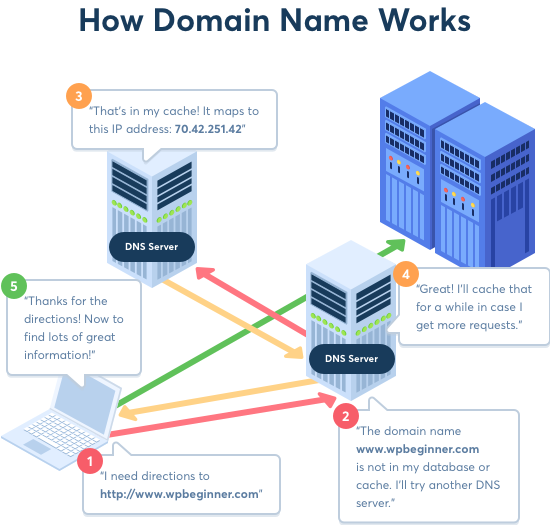
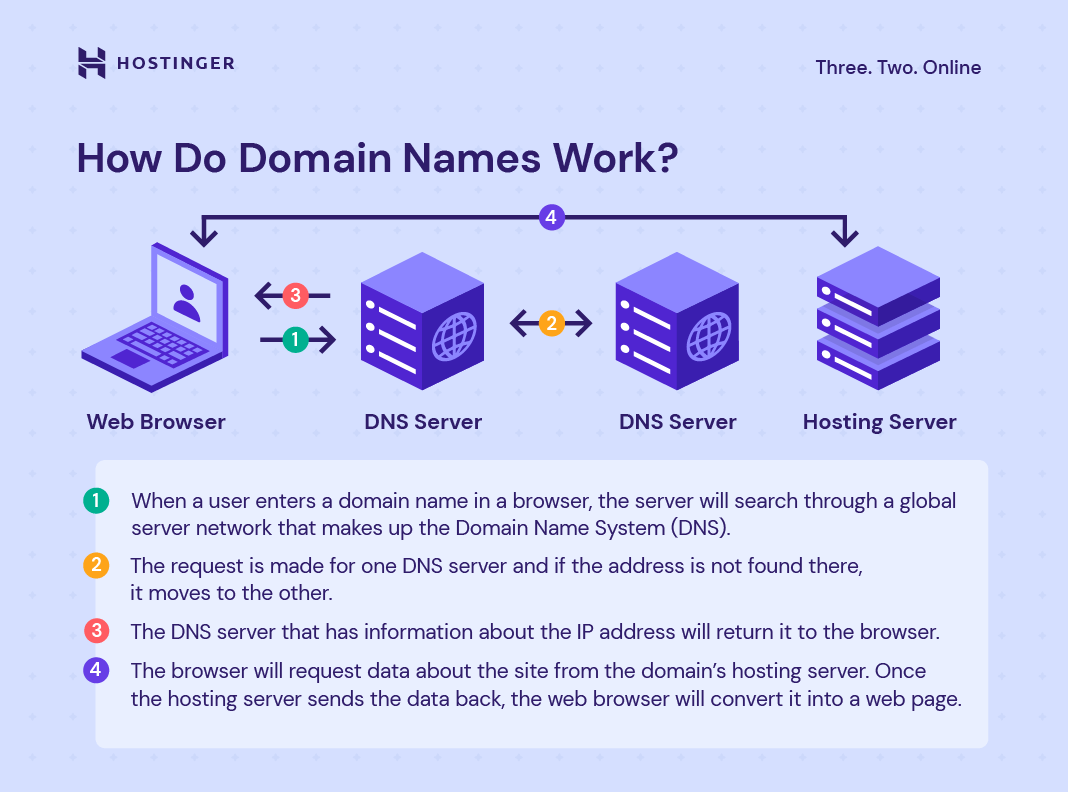
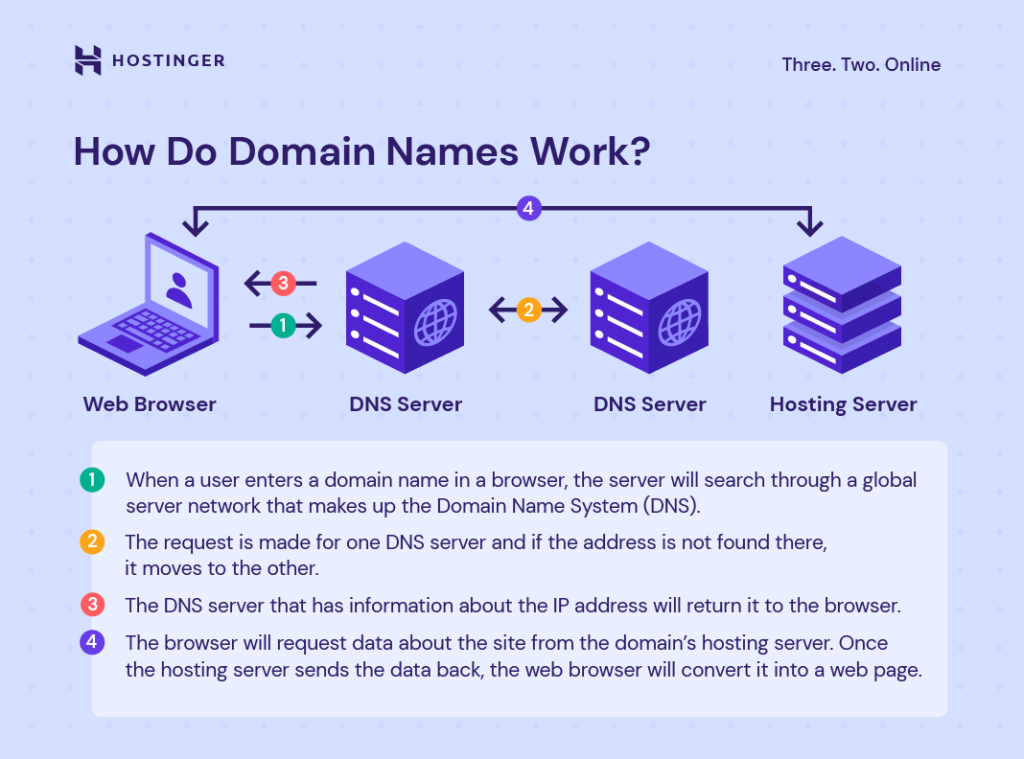
Dns Lookup Process
The DNS lookup process begins when you type a domain name into your browser. The browser sends a request to a DNS server. The DNS server then looks up the IP address associated with the domain name.
If the DNS server has the IP address cached, it returns it to the browser. If not, the server contacts other DNS servers to find the IP address. Once found, the IP address is sent back to the browser.
The browser uses the IP address to connect to the web server. The web server then sends the requested web page to your browser.
Registering A Domain Name
Registering a domain name is a crucial step in establishing your online presence. It acts as your website’s address on the internet. Without a domain name, people cannot find your website. The process may seem technical, but it is straightforward.
Choosing A Domain Registrar
Begin by selecting a domain registrar. A domain registrar is a company that manages the reservation of domain names. Popular registrars include GoDaddy, Namecheap, and Google Domains. Compare their prices and features.
Look for registrars that offer good customer support. Ensure they have a user-friendly interface. Read reviews to understand their reputation. Make an informed choice.
Steps To Register
First, check if your desired domain name is available. Use the search tool on the registrar’s website. Enter the domain name you want. The tool will show if it is taken or available.
Next, select the domain name you want to register. Add it to your cart. Proceed to the checkout page.
Fill in your personal information. This usually includes your name, address, and email. Some registrars offer privacy protection. This hides your personal details from the public database.
Choose the registration period. You can register a domain for one year or more. Longer periods may offer discounts.
Review your order. Ensure all details are correct. Complete the payment process. Use a secure payment method.
Once payment is confirmed, you will receive a confirmation email. Your domain name is now registered. You can start building your website.
Types Of Domain Names
Understanding the different types of domain names is crucial. Each type serves a specific purpose and has its own unique characteristics. This section will help you understand the two main categories: Generic TLDs and Country Code TLDs.
Generic Tlds
Generic Top-Level Domains (gTLDs) are the most common type. These include .com, .net, .org, and many others. They are not tied to any specific country. Businesses and individuals worldwide use gTLDs. They are versatile and widely recognized.
Country Code Tlds
Country Code Top-Level Domains (ccTLDs) are unique to each country. Examples include .us for the United States and .uk for the United Kingdom. These domains often signify that the website is local. They can boost local SEO. They are great for businesses targeting specific regions.
Transferring A Domain Name
Transferring a domain name means moving it from one registrar to another. This process is common for various reasons. Understanding the transfer process is essential. It’s a straightforward task if you follow the steps carefully.
Reasons For Transfer
There are several reasons to transfer a domain name. One reason is to get better customer service. Some registrars offer better support than others. Another reason is to find a more affordable price. Some registrars charge less for renewals.
Security is also a reason for transferring. Some registrars have better security features. Transferring can also help consolidate all domains under one registrar. This makes management easier.
Transfer Process
The transfer process starts with unlocking the domain. This allows it to be transferred. Next, you need an authorization code. This code verifies the transfer.
Once you have the code, you can request the transfer. The new registrar will ask for the code. Then, the current registrar will confirm the transfer. This can take a few days.
After confirmation, the domain moves to the new registrar. You will receive a notification. The process is complete. Now, you can manage the domain with the new registrar.
Domain Name Security
Understanding domain name security is crucial for protecting your online presence. A domain name is an address where Internet users can access your website. Just like any other digital asset, it needs protection from various threats. Let’s dive into common threats and protection measures.
Common Threats
Domain names face several common threats that can compromise their security. Here are a few:
- Domain Hijacking: Attackers gain control of your domain by stealing login details.
- Phishing: Fake websites trick users into providing personal information.
- DNS Spoofing: Hackers redirect traffic to malicious sites.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Intercepting communication between your site and users.
Protection Measures
Implementing protection measures can safeguard your domain name from threats. Here are some effective strategies:
- Use Strong Passwords: Create complex passwords for your domain registrar account.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Adds an extra layer of security to your account.
- Keep Contact Information Updated: Ensures you receive important notifications about your domain.
- Lock Your Domain: Prevents unauthorized transfers or modifications.
- Regularly Monitor Your Domain: Look for suspicious activities or changes.
By following these steps, you can enhance your domain name security and protect your digital identity.
Credit: dorik.com
Future Of Domain Names
The future of domain names is evolving rapidly. As the internet grows, new trends and challenges arise. Understanding these changes can help businesses and individuals stay ahead.
Emerging Trends
New domain extensions are becoming popular. These include .tech, .blog, and .shop. They offer more options for unique and specific names. Voice search is also influencing domain choices. Short and memorable names are easier for voice assistants to recognize. Blockchain domains are gaining traction. They provide more security and less censorship. These trends show how the domain name landscape is shifting.
Potential Challenges
With more domain options, choosing the right one can be difficult. It’s important to pick a name that stands out and is easy to remember. Cybersecurity threats are another concern. As technology advances, so do hacking techniques. Protecting domain names from theft and misuse is crucial. The cost of premium domain names is rising. This can be a barrier for small businesses and individuals. Adapting to these challenges is key to maintaining a strong online presence.
Credit: www.hostinger.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Domain Name?
A domain name is a website’s address on the internet. It is the text that users type into a browser’s URL bar to visit your site.
How Does A Domain Name Work?
A domain name works by translating human-friendly names into IP addresses. This allows browsers to locate and load websites.
Why Are Domain Names Important?
Domain names are important because they provide a memorable, user-friendly way to access websites. They help establish your online presence and brand identity.
How Do I Register A Domain Name?
To register a domain name, you need to choose a registrar. Then, check the availability of your desired name and complete the registration process.
Conclusion
Understanding domain names is essential for navigating the internet. They act as your website’s address, guiding users to your content. Choosing the right domain name can make your site memorable. Registering and managing it is straightforward with the right tools.
Remember, a clear domain boosts your online presence. Keep your domain name simple and relevant. This ensures users find you easily. Now, go ahead and secure that perfect domain name for your website. Happy web surfing!