Artificial Intelligence (AI) has a rich and intriguing history. It spans decades of innovation and discovery.
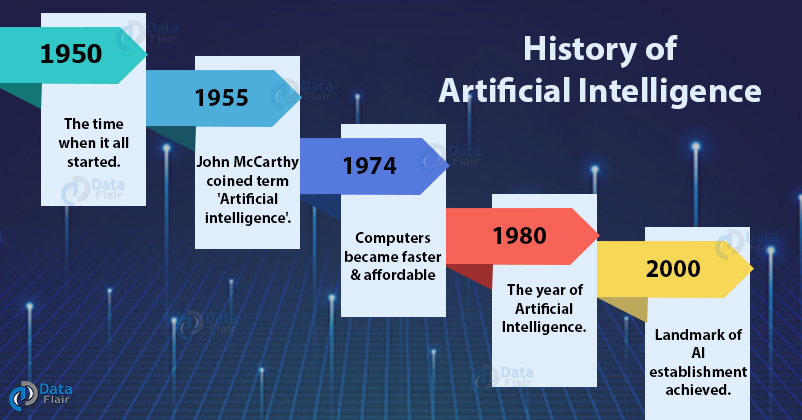
The journey of AI began in the mid-20th century. Pioneers like Alan Turing and John McCarthy set the groundwork. Turing’s question, “Can machines think? ” Sparked curiosity. The term “Artificial Intelligence” was born in 1956. McCarthy coined it during the Dartmouth Conference.
Since then, AI has evolved rapidly. It moved from simple programs to complex algorithms. Early AI focused on problem-solving and reasoning. Today, it impacts various fields like healthcare, finance, and robotics. Understanding AI’s history helps us appreciate its present and future. Dive in to explore the milestones and breakthroughs that shaped AI. Discover how far we’ve come in this fascinating field.
Early Concepts
Understanding the history of Artificial Intelligence (AI) begins with exploring its early concepts. These foundational ideas date back to ancient times and have evolved through various philosophical and mythological narratives.
Ancient Myths
Many ancient civilizations imagined artificial beings. These myths often featured mechanical servants or intelligent automata. For example, in Greek mythology, Hephaestus, the god of blacksmiths, created Talos, a giant bronze man. Talos protected Crete from invaders.
Similarly, in Chinese mythology, there is the story of Yan Shi, an engineer who created a life-sized, human-like figure. This figure could move and mimic human actions. These stories reflect early human fascination with creating intelligent beings.
Philosophical Foundations
Early concepts of AI are also rooted in philosophy. Ancient Greek philosophers like Plato and Aristotle pondered the nature of human thought and intelligence. They explored whether machines could replicate human reasoning.
In the 17th century, philosopher René Descartes proposed that animals and humans could be seen as complex machines. His ideas laid the groundwork for the mechanistic view of the mind. This view is crucial in understanding AI’s theoretical foundations.
Later, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz introduced the concept of a universal language and a calculating machine. Leibniz believed that human reasoning could be reduced to calculations. His ideas influenced the development of modern computing and AI.
| Philosopher | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Plato | Explored nature of human thought |
| Aristotle | Investigated human reasoning |
| René Descartes | Proposed mechanistic view of mind |
| Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz | Concept of universal language |
These early ideas and stories reflect humanity’s long-standing curiosity about artificial intelligence. They provide a rich backdrop to the modern development of AI.
Credit: data-flair.training
Mathematical Foundations
The history of artificial intelligence (AI) is deeply rooted in mathematics. The mathematical foundations of AI provide the necessary tools and concepts for building intelligent systems. These foundations include various branches of mathematics that have contributed to the development of AI over the years. Two key areas are Boolean Algebra and Turing Machines.
Boolean Algebra
Boolean Algebra is a branch of algebra that deals with true or false values. It is named after George Boole, who introduced this concept in the mid-19th century. Boolean Algebra is fundamental to the design of digital circuits and computer algorithms.
In Boolean Algebra, variables represent logical statements. These statements can have values of either true (1) or false (0). The basic operations in Boolean Algebra are:
- AND (conjunction)
- OR (disjunction)
- NOT (negation)
Here is a simple example:
| A | B | A AND B | A OR B | NOT A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
These simple operations form the basis of more complex logical expressions used in computer science and AI.
Turing Machines
Turing Machines were introduced by Alan Turing in 1936. They are abstract computational devices that help in understanding the limits of what can be computed. A Turing Machine consists of:
- A tape divided into cells
- A head that reads and writes symbols on the tape
- A set of states, including a start state and one or more halt states
The machine operates by following a set of rules. These rules determine how the machine transitions from one state to another based on the current state and the symbol it reads from the tape. The tape can be infinitely long, allowing for unlimited computation.
Turing Machines are important because they provide a model for understanding computation. They help in defining what problems are computable and form the theoretical basis for modern computers.
Both Boolean Algebra and Turing Machines are crucial in the development of AI. They provide the foundational concepts and tools that enable the creation of intelligent systems.
Birth Of Ai
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has a fascinating history. The Birth of AI marked a significant moment. It was a time of groundbreaking discoveries. Let’s dive into the key events that shaped AI.
Dartmouth Conference
The Dartmouth Conference took place in 1956. It was a pivotal moment in AI’s history. This event is often considered the birth of AI as a field.
At Dartmouth College, ten scientists gathered. They discussed the possibility of creating machines that could think. This meeting was led by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon. They proposed that “every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence can in principle be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it.”
This conference laid the foundation. It set the stage for future AI research and development. The discussions and ideas from this meeting led to many significant advancements in AI.
Early Pioneers
Several early pioneers played crucial roles. They were the driving force behind AI’s development.
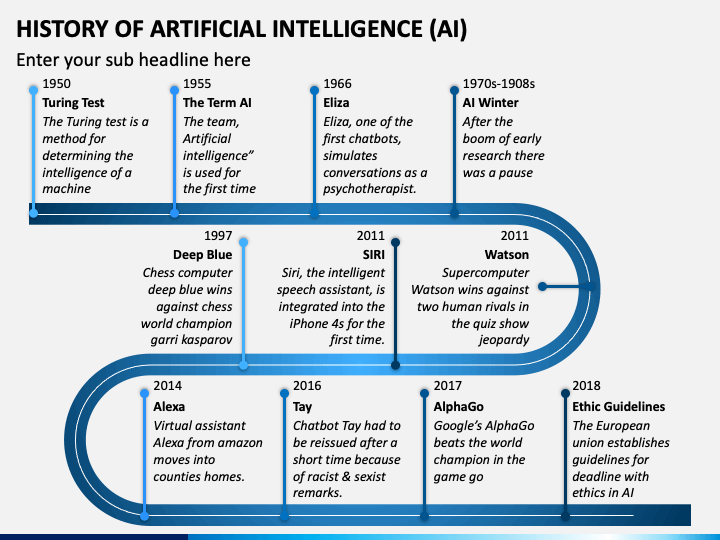
- Alan Turing: Known for the Turing Test. He proposed that if a machine could carry on a conversation indistinguishable from a human, it could be considered intelligent.
- John McCarthy: Coined the term “Artificial Intelligence.” He organized the Dartmouth Conference and developed the Lisp programming language, which became a standard for AI research.
- Marvin Minsky: Co-founder of the MIT AI Lab. He made significant contributions to AI, including work on neural networks and robotics.
- Herbert Simon and Allen Newell: Developed the Logic Theorist, considered the first AI program. It proved mathematical theorems and demonstrated the potential of AI.
These pioneers paved the way. Their contributions are the foundation of modern AI.
Credit: medium.com
Golden Years
The Golden Years of Artificial Intelligence (AI) spanned from the mid-1950s to the 1970s. This era saw rapid advancements and the establishment of fundamental AI concepts. Researchers focused on building intelligent machines that could perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence. Two key developments during this period were Symbolic AI and Expert Systems.
Symbolic Ai
Symbolic AI, also known as “Good Old-Fashioned AI” (GOFAI), emerged in the 1950s. It aimed to use symbols to represent knowledge and rules to process information. Researchers believed that intelligence could be represented through symbolic manipulation.
Programs like the Logic Theorist, developed by Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon in 1956, showcased this approach. The Logic Theorist was capable of proving mathematical theorems. It used a tree search algorithm to explore possible solutions.
Another milestone was the creation of the General Problem Solver (GPS) by the same team. GPS could solve a wide range of problems by representing them symbolically. This demonstrated the potential of symbolic AI to tackle various intellectual tasks.
Expert Systems
Expert Systems emerged in the 1970s as a practical application of AI. These systems aimed to replicate the decision-making abilities of human experts in specific domains. They used a vast knowledge base and a set of rules to draw conclusions.
One of the first successful expert systems was DENDRAL, developed in the 1960s. DENDRAL helped chemists identify molecular structures using mass spectrometry data. It significantly improved the accuracy and speed of analysis.
Another notable system was MYCIN, created in the early 1970s. MYCIN assisted doctors in diagnosing bacterial infections and recommending antibiotics. It used a rule-based approach, considering symptoms and medical history to provide accurate recommendations.
| Expert System | Domain | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| DENDRAL | Chemistry | Improved molecular structure identification |
| MYCIN | Medicine | Enhanced diagnosis and treatment |
Expert Systems demonstrated the practical utility of AI. They paved the way for future advancements in various fields. These systems showcased the potential of AI to augment human expertise.
Ai Winters
The history of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is marked by periods known as AI Winters. These were times when interest and funding in AI significantly declined. During these periods, AI research and development faced major setbacks. Let’s dive into the key factors that contributed to these AI Winters.
Funding Cuts
One of the main reasons for AI Winters was the significant funding cuts. Governments and organizations reduced or eliminated financial support for AI projects. This decrease in funding happened because early AI systems did not meet expectations. Over-promised results led to disappointment. As a result, investors lost confidence.
For example, in the 1970s, the US and British governments cut funding for AI research. They were disappointed by the slow progress. This led to a significant halt in AI advancements. The same happened in the late 1980s. Another wave of funding cuts followed unmet expectations.
Technical Challenges
Another factor was the technical challenges faced by researchers. Early AI systems struggled with basic tasks. They lacked the computational power and data needed to perform well. This made it hard to create useful AI applications.
Researchers also faced issues with natural language processing and machine learning algorithms. Early AI struggled to understand and generate human language. Machine learning algorithms were not advanced enough. They couldn’t learn from data effectively.
| Technical Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Computational Power | Limited AI’s ability to process data |
| Data Availability | Insufficient data for training AI models |
| Natural Language Processing | AI struggled with human language |
| Machine Learning Algorithms | Ineffective learning from data |
The combination of funding cuts and technical challenges led to AI Winters. These periods were tough for AI researchers. They had to find new ways to overcome these obstacles. Despite these setbacks, AI research continued. Eventually, it led to the advancements we see today.
Resurgence
The history of Artificial Intelligence has seen many ups and downs. After a period of doubt and slow progress, AI experienced a resurgence in the early 21st century. This period is marked by significant advancements and widespread adoption. Let’s explore the key factors that fueled this resurgence.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning became a driving force behind AI’s resurgence. Unlike traditional programming, where rules are explicitly coded, machine learning allows systems to learn from data. This approach led to more accurate predictions and decisions.
Key developments in machine learning include:
- Neural Networks
- Deep Learning
- Natural Language Processing
These techniques improved the ability of machines to understand and generate human language, recognize images, and play complex games.
Big Data Influence
The rise of big data played a crucial role in AI’s resurgence. With the explosion of digital information, there was a vast amount of data available for analysis. This abundance of data enabled more sophisticated machine learning models.
Big data’s influence can be seen in:
| Area | Impact |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Improved diagnosis and treatment plans |
| Finance | Better fraud detection and risk management |
| Retail | Enhanced customer experiences and inventory management |
These advancements in machine learning and big data have been pivotal in the resurgence of AI, propelling it into various sectors and transforming industries.
Modern Ai
Modern AI has transformed the way we interact with technology. The advancements in AI today are remarkable. This section explores key elements of modern AI, such as deep learning and neural networks.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning. It uses algorithms inspired by the human brain. These algorithms are called artificial neural networks. They learn from large amounts of data. Deep learning powers many AI applications. Examples include image and speech recognition. It is crucial for self-driving cars and medical image analysis. Deep learning has made AI more accurate and efficient.
Neural Networks
Neural networks are at the core of deep learning. They consist of layers of nodes. These nodes act like neurons in the brain. Each layer processes information. The processed data is passed to the next layer. This process continues until the final output is generated. Neural networks can learn complex patterns. They improve their performance over time. This makes them ideal for tasks like language translation and predictive analytics.
Future Prospects
The future prospects of Artificial Intelligence (AI) look promising. AI continues to evolve and impact various sectors. From healthcare to transportation, its applications are vast. But what lies ahead for this innovative technology? Let’s explore some key areas.
Ethical Considerations
AI’s growth brings ethical concerns. Data privacy stands as a major issue. How will AI handle sensitive information? Bias in AI algorithms also raises questions. Can we ensure fair and unbiased decision-making? These ethical challenges need addressing. Clear guidelines and regulations are essential. They will help maintain public trust in AI.
Ai In Everyday Life
AI is becoming part of daily routines. Smart assistants like Alexa and Siri are examples. They simplify tasks and provide information. AI helps in personalized recommendations. Think of Netflix and Spotify. They suggest content based on user preferences. AI also enhances online shopping. It offers product recommendations and improves customer service.
In healthcare, AI assists in diagnosis and treatment. It analyzes medical data quickly. This leads to faster and more accurate results. AI also plays a role in education. It offers personalized learning experiences. Students receive tailored content that suits their learning pace.
Transportation is another area benefiting from AI. Self-driving cars are becoming a reality. They promise safer and more efficient travel. AI also optimizes traffic management. It reduces congestion and improves road safety.
These examples show AI’s potential in everyday life. Its applications are vast and growing. The future holds exciting possibilities for AI integration.
Credit: library.icc.edu
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Origin Of Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) originated in the 1950s. Researchers aimed to create machines that could mimic human intelligence. Early work included the development of algorithms and neural networks.
Who Is Considered The Father Of Ai?
John McCarthy is often called the father of AI. He coined the term “Artificial Intelligence” in 1956. His work laid the foundation for modern AI research.
How Has Ai Evolved Over The Years?
AI has evolved from simple algorithms to complex neural networks. Early AI focused on rule-based systems. Modern AI uses machine learning and deep learning techniques.
What Were The Significant Milestones In Ai History?
Significant milestones include the creation of the Turing Test, development of the first neural networks, and IBM’s Deep Blue defeating a chess champion. These milestones advanced AI capabilities.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence has a rich and fascinating history. From early concepts to modern advancements, AI has evolved significantly. Each milestone has shaped the technology we see today. The journey continues, promising more exciting developments. Understanding AI’s past helps us appreciate its future potential.
Stay curious, and keep exploring AI’s incredible world.